- Casablanca. Morocco
- 147 boulevard SMIHA, office 201.
- contact@business-setup.ma
- Office Hour: 09:00am - 6:00pm
Why Invest In Morocco- investment services in moroco - investment funds
7 Top Reasons
Cost Competitiveness
Only 14km south of Europe, Morocco is a competitive platform for export :
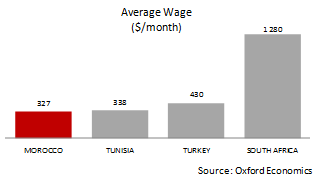
Low Wages : The average wage is 327$/month.
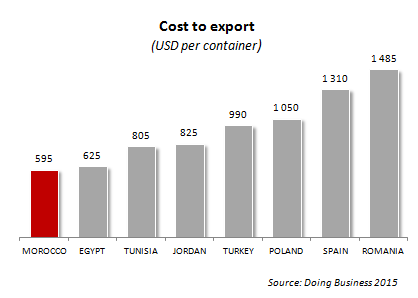
Competitive costs to export : 595 USD/container/ according to the World Bank data, that is the 12th most competitif rate world wide.
This cost includes for a 20-foot container, all fees charged by government agencies and the private sector to a trader in the process of exporting and importing the goods. These include but are not limited to costs for documents, administrative fees for customs clearance and inspections, customs broker fees, port-related charges and inland transport costs. The cost does not include customs tariffs and duties or costs related to sea transport. Source: Doing Business Report.
Low Tax rates : Taxes paid by companies represent only 49,3% of their profit
The total tax rate measures the amount of taxes and mandatory contributions borne by the business in the second year of operation, expressed as a share of commercial profit Source: Doing Business Report.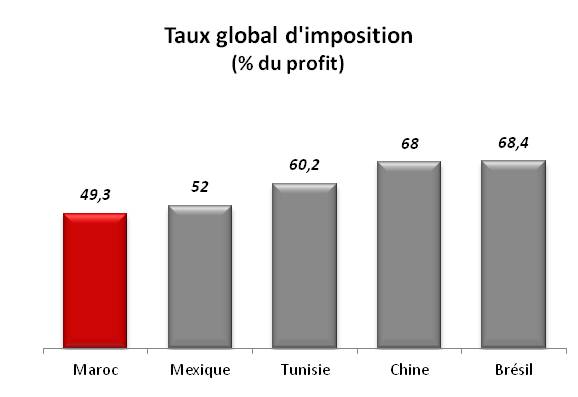
Source: Doing Business 2016
Strong and Stable Macroeconomic Performances
Preserving macroeconomic stability is a major concern for Moroccan governments. Several actions and structural reforms have been undertaken to put the country on the path of strong and sustainable growth:
Access to new growth levels
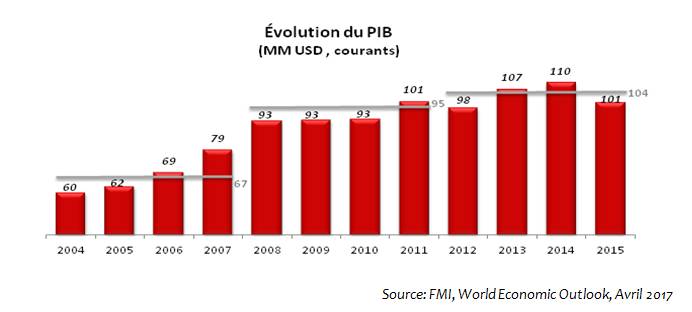
A continuously growing economy with an average growth rate of 4% over the period 2004-2015.
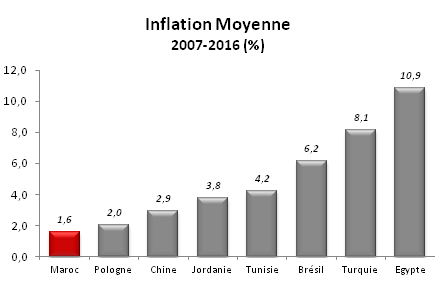
Controlled inflation
Inflation is maintained below 2% despite the rising prices of oil and raw materials.
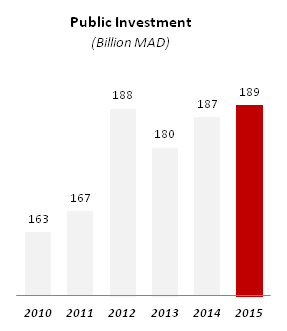
Growth driven by domestic demand and public investment
Household consumption grew by an average 5% per year between 2010 and 2015 to reach MAD 568 billion (59 billion USD), while public investment grew by an average 3% per year during the same period to reach MAD 189 billion (20 billion USD)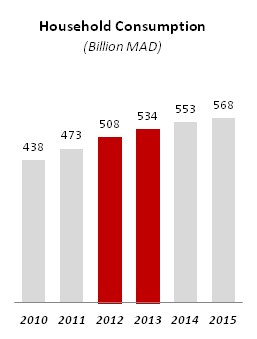
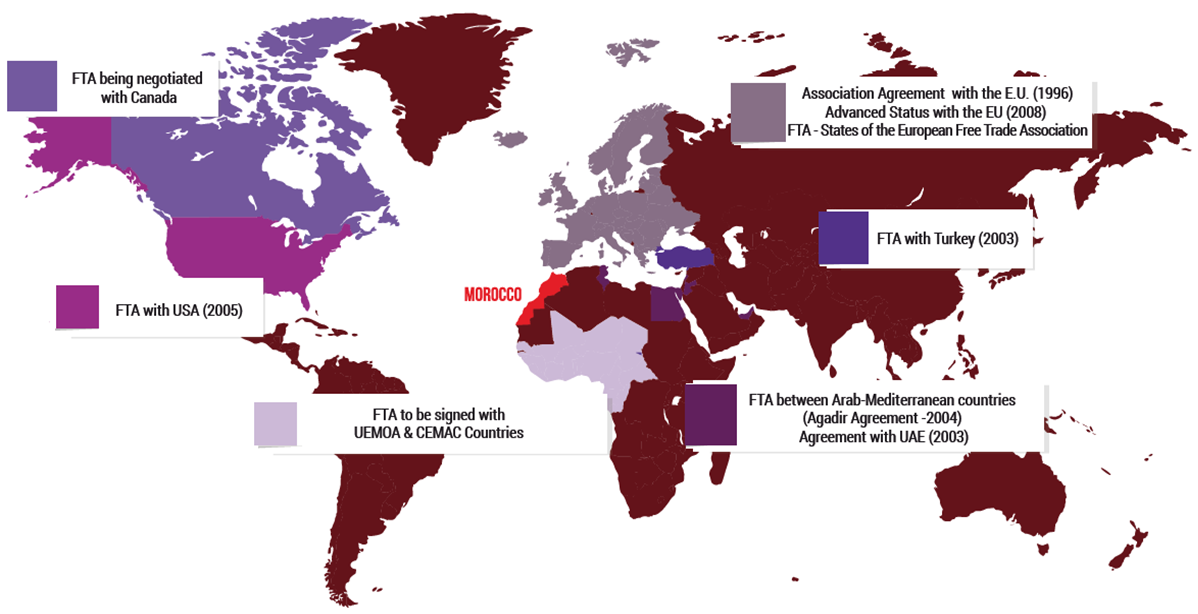
Free Trade Access to One Billion Consumers
As part of an overall market-opening strategy and liberalization , Morocco proceeded during the last decade to the establishment of a legal framework to boost its trade ties with more than 55 countries.
World Class Infrastructure
Morocco, 1st in Africa in terms of infrastructure quality according to Global competitivness Index-WEF 2016-2017 (Mauritius is considered as Dom-Tom)
For over a decade, Morocco launched large-scale projects aimed at elevating its infrastructure to international standards:
Tanger-Med Port : entered into service in 2007 with a total capacity of 8 million containers, in addition to professional real estate of over 5000 hectares, complements the overall port infrastructure consisting of 38 (13 foreign trade) ports meeting international standards.
Tanger Med en Bref
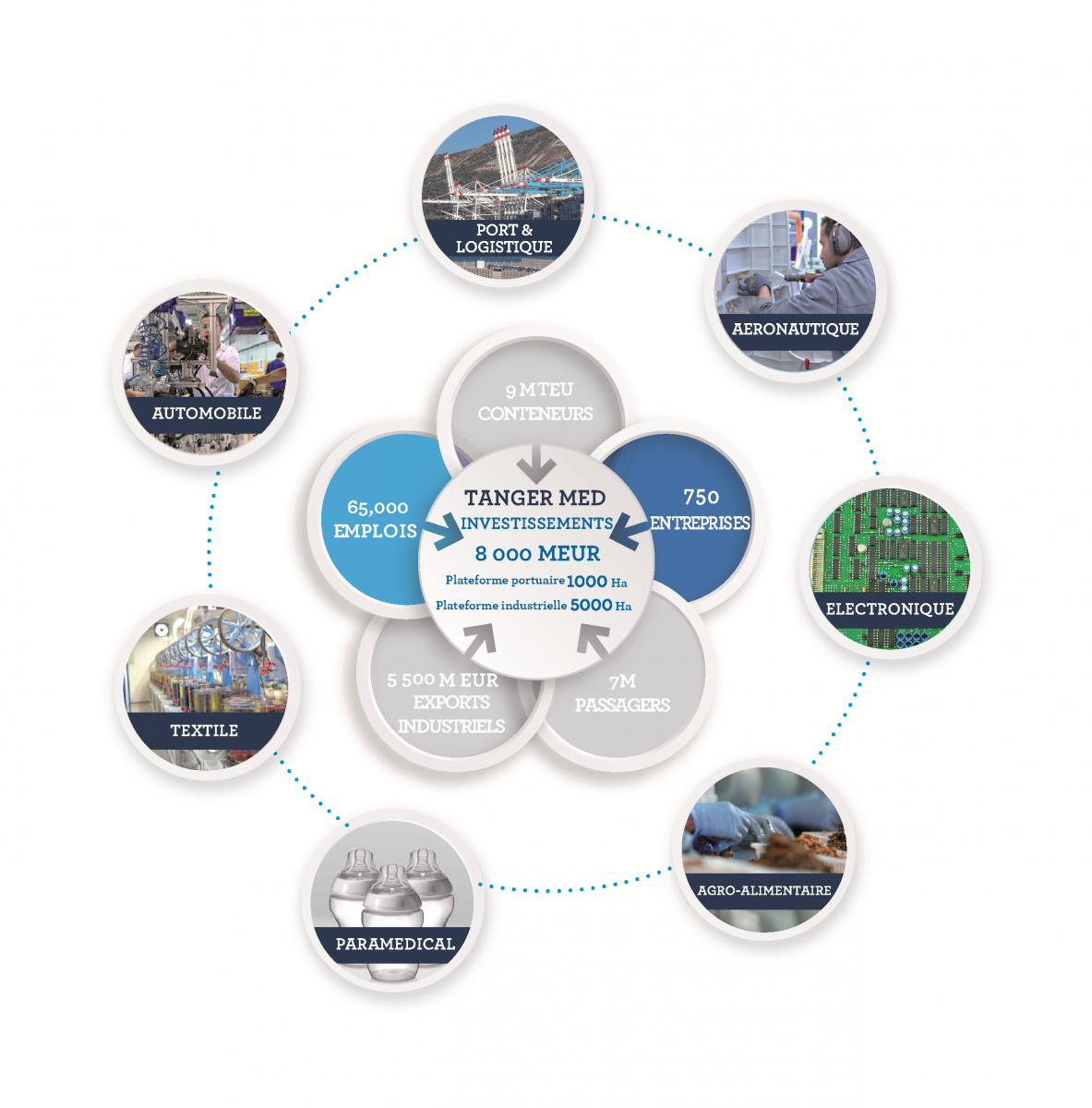
Source: TMSA
The Highway Network has grown exponentially to link the main Moroccan cities of over 400 000 inhabitants. It should reach 3000 km by2020.
Evolution of the highway network
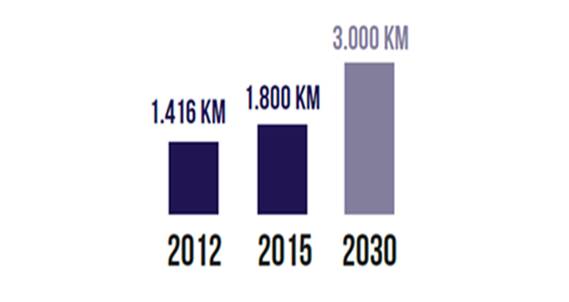
Source: Ministère de l’équipement, du transport et de la logistique
Thanks to an Open Sky policy, the 17 international airports in Morocco (largest airport hub in the region) are used by a multitude of international companies and are connected to major cities and economic platforms of world affairs.
Commercial air traffic by nature (2015)
| Airport | Accumulation Dec 2014 | Accumulation Dec 2015 | Var (%) | Part (%) |
| International | 15 579 863 | 15 845 933 | 1,71 | 90 |
| National | 1 715 008 | 1 763 814 | 2,85 | 10 |
| Overall total | 17 294 871 | 17 609 747 | + 1,82 |
Source: ONDA
A wide network of Economic activity zones (Industrial Integrated Platforms, Free zones, Agropoles, clusters,…)
Telecommunications infrastructure aux normes internationales: Avec trois opérateurs globaux (fixe, mobile, internet et data), le secteur des télécommunications au Maroc enregistre chaque année une activité intense et soutenue: avec un total de plus de 42 millions d’abonnés par an sur la période 2012-2016 contre 27 millions d’abonnés sur la période 2007-2011.
Evolution du parc mobile
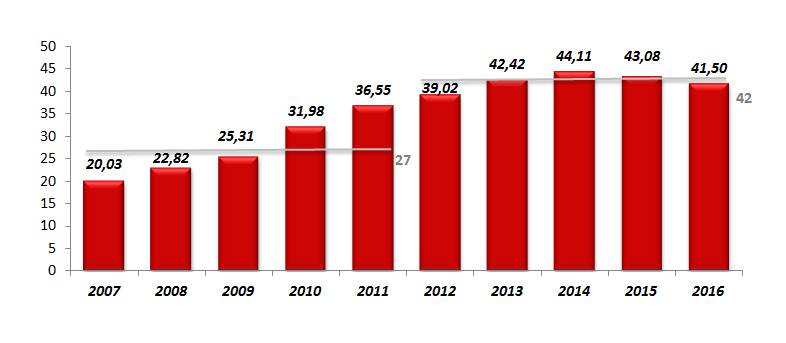
Source: ANRT
Telecommunications infrastructure meeting international standards. Three global operators (Fixed phone, mobile, Internet and data), the telecommunications sector in Morocco achieves every year an intense and sustained activity: 127% mobile penetration ( 2015) and 43 million clients.
Qualified Labor Force
In Morocco, human resources have all the ingredients to become the pivots of a competitive investment and value creator: education level, cultural openness, language skills and new technologies, commitment to entrepreneurship, adaptation capacity to change and competitive labor costs:
A young and active population:
Total population of 33,8 million inhabitants
64% of population aged under 34
6 million of young people aged 18 – 35
Active population of 12 million
Qualified Human Ressources:
More than 100 Universities and public schools
500 000 students in higher education
40 000 higher education graduates per year
Training of 25 000 engineers per year by 2020
Advanced linguistics capacities
Over 10 million french speakers
Over 6 million spanich speakers
Large penetration of English among young people and management staff
Vocation training adapted to market needs:
332 vocational training institutions
Training of 370,000 students (2014 – 2015)


Sectorial Plans
Morocco launched numerous strategic sectorial plans that ensure strong and sustainable economic growth. This reform momentum is marked by an innovative contracting approach and public private partnership advocating greater and coordinated participation of the private sector in the development of sectoral strategies and policies along with the funding of projects allowing to refocus the State’s role on its regulatory powers.
These strategies are part of a process to speed the development of strategic sectors like agriculture, fishery, mining, renewable energy, logistics and promising sectors such as automotive, aerospace and services with high added value.
Constantly improving business Climate
To promote the investment act, a particular attention is given to improving the business climate. A set of mechanisms to increase competition and transparency was put in place:
Simplification of administrative procedures for businesses
Strengthening the business law framework (law on competition and free pricing, law on economic interest groups, law on industrial and intellectual property …)
Improving regulatory transparency
Development and modernization of financial markets
Creation of the Business Environment National Committee
Creation of the Central Authority on the Prevention of Corruption
Creation of the Moroccan Office for Intellectual and Commercial Property
Promotion of the Charter on Corporate Social Responsibility
Source: Morocco Investment Development Agency

